In mathematics, the Fibonacci numbers commonly denoted Fn, form a sequence, called the Fibonacci sequence, such that each number is the sum of the two preceding ones, starting from 0 and 1. That is,
The sequence starts:
- 0, 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 21, 34, 55, 89, 144, ...
Under some older definitions, the value is omitted, so that the sequence starts with and the recurrence is valid for n > 2. In his original definition, Fibonacci started the sequence with
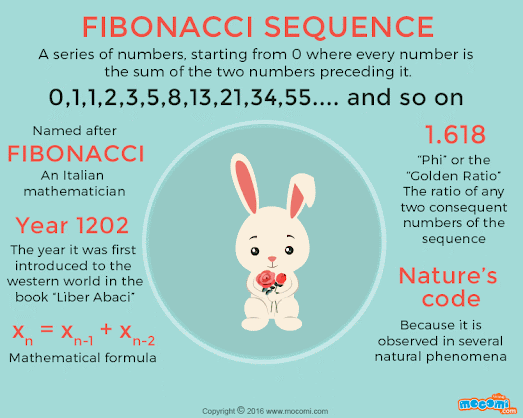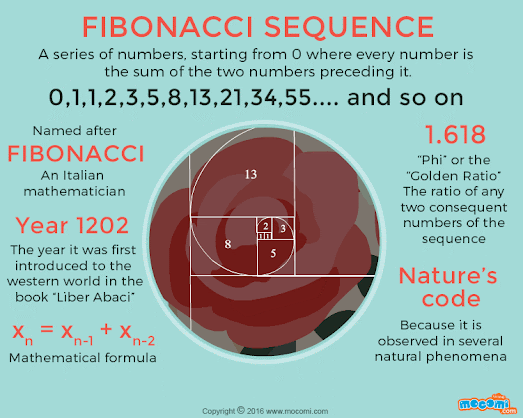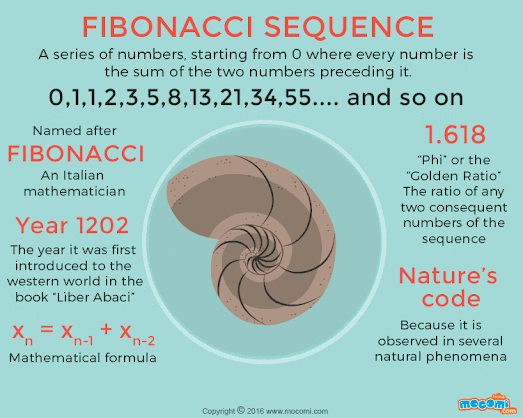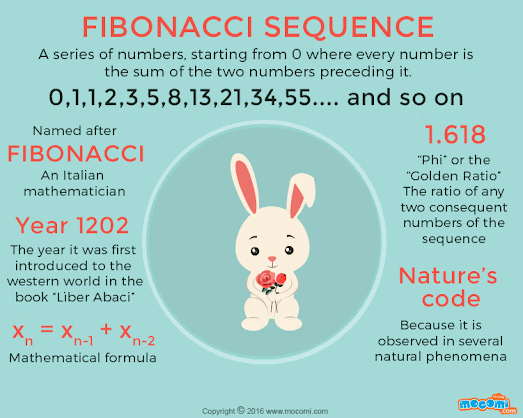
Fibonacci numbers are strongly related to the golden ratio: Binet's formula expresses the nth Fibonacci number in terms of n and the golden ratio and implies that the ratio of two consecutive Fibonacci numbers tends to the golden ratio as n increases.
Fibonacci numbers are named after the Italian mathematician Leonardo of Pisa, later known as Fibonacci. In his 1202 book Liber Abaci, Fibonacci introduced the sequence to Western European mathematics, although the sequence had been described earlier in Indian mathematics, as early as 200 BC in work by Pingala on enumerating possible patterns of Sanskrit poetry formed from syllables of two lengths.
Fibonacci numbers appear unexpectedly often in mathematics, so much so that there is an entire journal dedicated to their study, the Fibonacci Quarterly. Applications of Fibonacci numbers include computer algorithms such as the Fibonacci search technique and the Fibonacci heap data structure, and graphs called Fibonacci cubes used for interconnecting parallel and distributed systems.
They also appear in biological settings, such as branching in trees, the arrangement of leaves on a stem, the fruit sprouts of a pineapple, the flowering of an artichoke, an uncurling fern, and the arrangement of a pine cone's bracts.
The code for this problem is:
Program using while loop:
package com.fibonacci;
public class Fibonacci {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a = 0,b = 1,result = 0;
System.out.println("The fibonacci series is : ");
System.out.println(a);
while(result < 30) {
result = a + b;
a = b;
b = result;
System.out.println(+ result);
}
}
}
Program using for loop:
public class ForFibonacci {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a = 0, b = 1, result,i ,n = 10;
System.out.println("The first " +n+" terms of the fibonacci series are: ");
System.out.println(a);
for (i = 0;i<n;i++){
result = a + b;
a = b;
b = result;
System.out.println(+result);
}
}
}







No comments:
Post a Comment