A light-emitting diode(LED) is a two-terminal semiconductor light source. When sufficient current is applied across its terminals, electrons, and holes within the led combine and release energy in form of photons. The emission of these photons is seen as light. An old-fashioned light bulb wastes a lot of power by converting it into heat. LEDs are much smarter: they convert almost all their power into light, and they last almost indefinitely.
Things to remember when working with LEDs:
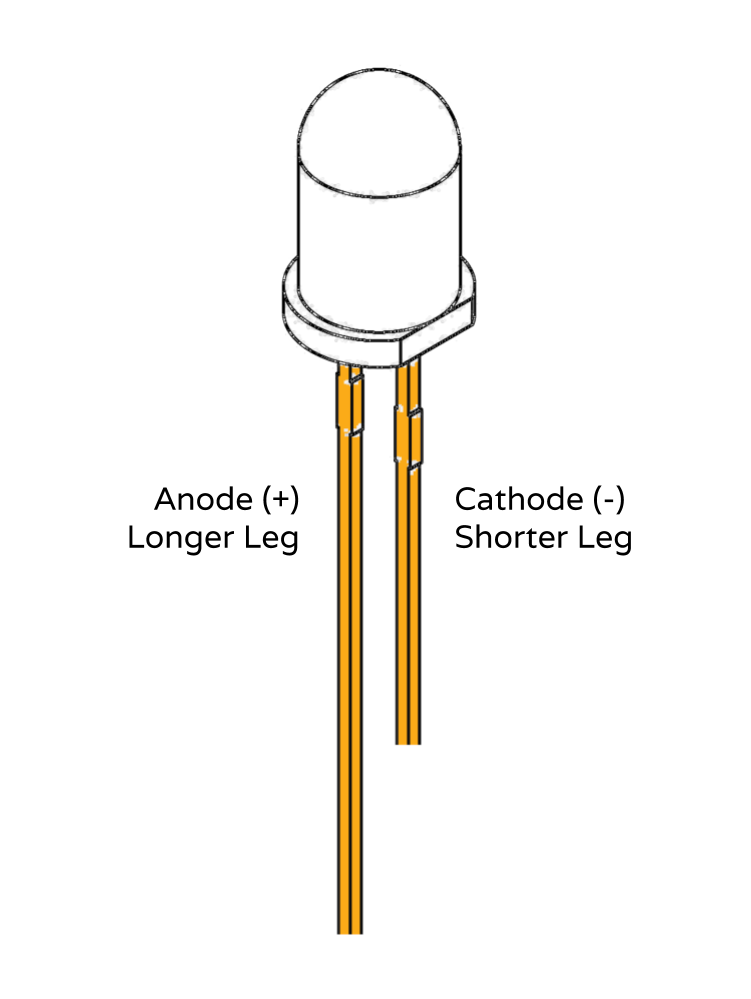
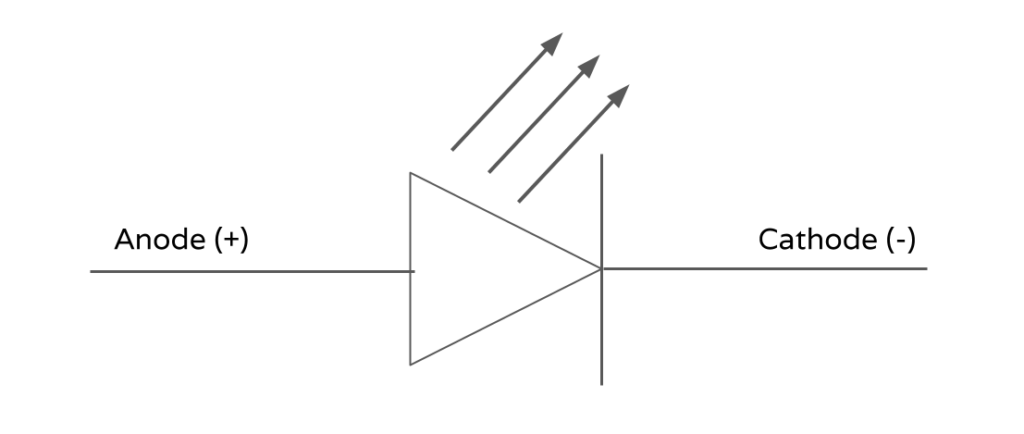
• The longer wire protruding from the LED (anode) must receive a more positive voltage than the shorter wire.
• The voltage difference between the long wire and the short wire must not exceed the limit stated by the manufacturer.
• The current passing through the LED must not exceed the limit stated by the manufacturer.


No comments:
Post a Comment